Lắc tay
Data Brokers’ Impact on the Internet of Things (IoT) Ecosystem

In today’s digital age, the seamless integration of technology into everyday life has given rise to a new dimension of connectivity. This section delves into the intricate mechanisms that facilitate the collection and exchange of personal information through networked gadgets. As these devices become more intertwined with our daily routines, understanding the underlying processes becomes crucial for safeguarding privacy and ensuring ethical practices.
Information Aggregators play a pivotal role in this ecosystem, acting as intermediaries that gather and manage vast amounts of personal data. These entities operate behind the scenes, often unnoticed, yet their influence on How to get off BlockShopper information is shared and utilized is profound. The focus here is on exploring the implications of their activities and the potential risks associated with the widespread use of connected devices.
Moreover, the proliferation of networked gadgets has transformed the way we interact with technology. From smart home appliances to wearable fitness trackers, these devices generate a continuous stream of data that is both valuable and sensitive. This section will examine the challenges and opportunities presented by this data deluge, highlighting the need for robust frameworks to protect individual rights and foster a secure digital environment.
Ultimately, the aim is to provide a comprehensive overview of the current state of affairs, shedding light on the complex interplay between information aggregators and the devices that populate our connected world. By understanding these dynamics, we can better prepare for the future, ensuring that the benefits of technological advancement are balanced with the protection of personal privacy.
Understanding Information Aggregators
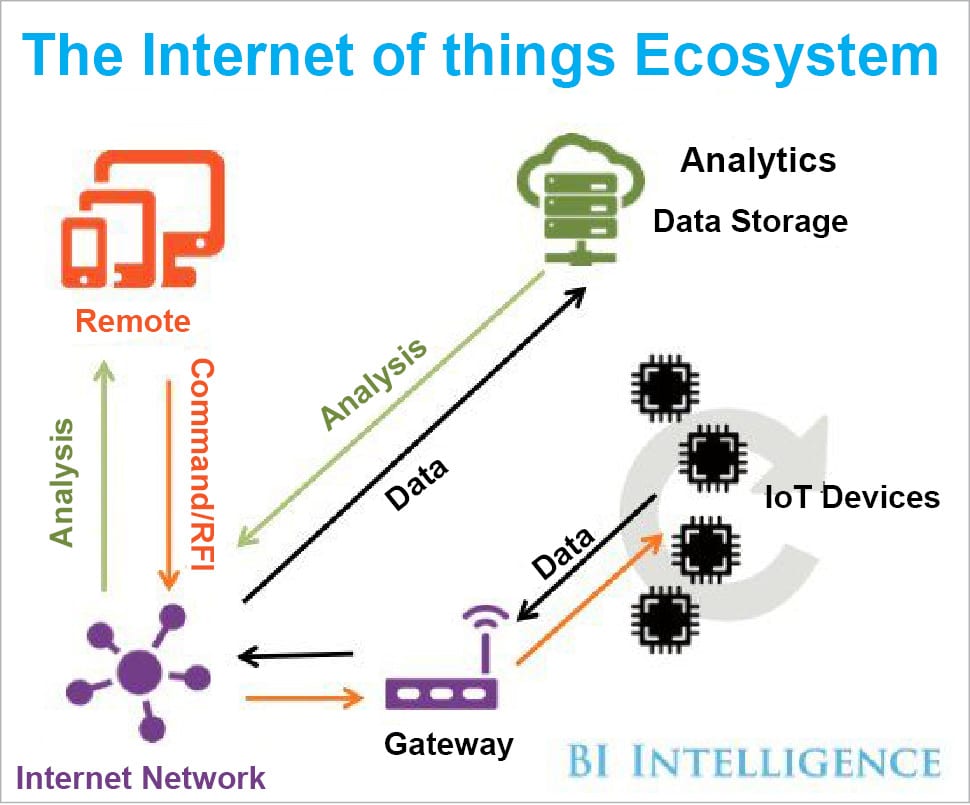
This section delves into the fundamental concepts surrounding entities that collect and manage vast amounts of personal information. It explores their functions, significance, and the mechanisms through which they operate within the digital ecosystem.
Information aggregators play a pivotal role in the contemporary digital landscape. They are entities that gather, analyze, and sell personal details to interested parties. This process is crucial for various industries, including marketing, finance, and security sectors.
- Collection of Personal Details: These entities gather information from multiple sources, including social media, public records, and online transactions.
- Analysis and Segmentation: The collected information is analyzed to identify patterns and segmented based on various criteria such as demographics, purchasing behavior, and online activities.
- Sale of Insights: The processed information is then sold to businesses, researchers, and government agencies, enabling them to make informed decisions based on market trends and consumer behavior.
The role of information aggregators extends beyond mere data collection and sales. They contribute to the efficiency of marketing campaigns, enhance financial risk assessment, and support law enforcement efforts by providing valuable insights derived from aggregated personal details.
Understanding the operations and impacts of these entities is essential for consumers, businesses, and policymakers alike. It helps in formulating strategies to protect personal privacy, regulate data usage, and leverage information responsibly within the digital economy.
Definition and Role of Information Aggregators

This section delves into the operational mechanics of entities that collect and manage vast amounts of personal information. These entities play a crucial role in the digital ecosystem, facilitating the exchange of information between various stakeholders. Understanding how they function is essential for comprehending their impact on privacy, security, and market dynamics.
Information aggregators operate through several key processes:
- Collection of Information: These entities gather personal details from multiple sources, including public records, online activities, and commercial transactions. This collection is often automated, utilizing sophisticated algorithms and data mining techniques.
- Storage and Management: The collected information is stored in large databases, which are managed using advanced data management systems. These systems ensure the integrity, security, and accessibility of the information.
- Analysis and Segmentation: Information is analyzed to identify patterns and trends. It is then segmented based on various criteria such as demographics, interests, and purchasing behavior. This segmentation helps in creating targeted marketing strategies.
- Distribution and Sale: The segmented information is then made available to interested parties, typically businesses looking to enhance their marketing efforts or improve their services. This distribution can be through direct sales or through subscription-based models.
- Compliance and Regulation: Entities must adhere to legal frameworks governing the collection, use, and distribution of personal information. This includes obtaining necessary permissions and ensuring that the information is used ethically and responsibly.
The operational framework of information aggregators is complex and multifaceted, involving technological, legal, and ethical considerations. As the digital landscape evolves, these entities continue to adapt, integrating new technologies and adjusting to regulatory changes to maintain their relevance and effectiveness in the market.
How Information Aggregators Operate
This section delves into the operational mechanics of entities that collect and manage vast amounts of personal information. It explores the processes through which these entities gather, analyze, and distribute sensitive details, often without direct consumer consent.
Information aggregators typically operate through a series of interconnected steps that involve data acquisition, processing, and distribution. Here’s a detailed breakdown of these operations:
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Acquisition | Entities collect personal information from various sources, including social media, public records, and online transactions. This data is often gathered through automated systems and third-party partnerships. |
| Processing | Once collected, the information is processed to extract relevant details and patterns. This involves using advanced algorithms and analytics tools to categorize and refine the data for specific uses. |
| Distribution | Processed information is then sold or shared with interested parties, such as marketers, researchers, and other businesses. This distribution can occur through direct sales or via online platforms that facilitate data exchanges. |
The operational model of information aggregators is complex and multifaceted, involving a blend of technology, legal frameworks, and market dynamics. Understanding these operations is crucial for assessing their impact on privacy and security in the digital age.
Legal Framework Governing Data Brokers
This section delves into the regulatory landscape that shapes the operations of information aggregators. It explores how legislative measures and compliance requirements influence the collection, processing, and distribution of personal information in the digital realm.
The legal environment for information aggregators is complex, involving a patchwork of federal and state laws. These regulations aim to protect consumer privacy while allowing for the legitimate use of collected information. Below is a summary of key legislative components that impact the industry:
| Legislation | Key Provisions | Impact on Information Aggregators |
|---|---|---|
| General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) | Applies to all companies processing the personal data of individuals residing in the EU, regardless of the company’s location. | Requires explicit consent for data collection, stringent data protection standards, and the right to erasure. |
| California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) | Grants California residents the right to know what personal information is collected about them, the right to delete that information, and the right to opt-out of its sale. | Imposes new obligations on businesses to disclose data collection practices and respect consumer rights regarding personal information. |
| Federal Trade Commission Act | Empowers the FTC to prevent unfair or deceptive acts or practices in or affecting commerce. | Provides a framework for regulating information aggregators who engage in deceptive data practices. |
Compliance with these regulations is critical for information aggregators to avoid legal repercussions and maintain consumer trust. As the digital landscape evolves, so too does the regulatory framework, necessitating ongoing adaptation and vigilance by those in the information aggregation sector.
IoT Information Managers: A New Frontier
In recent years, a novel sector has emerged within the expansive realm of digital technology, focusing on the collection, management, and utilization of information generated by interconnected devices. This sector, often referred to as IoT information managers, represents a significant shift in how we handle and leverage digital data, particularly in the context of smart devices and systems.
The rise of these information managers is driven by several key factors:
- Increased Connectivity: With the proliferation of smart devices, the volume of information being generated and shared across networks has skyrocketed, necessitating specialized entities to manage this influx.
- Technological Advancements: Advances in data processing and storage technologies have made it feasible to collect and analyze vast amounts of information in real-time, enabling more effective management strategies.
- Business and Consumer Demand: Both businesses and consumers are increasingly seeking efficient ways to utilize the data generated by their devices, driving the demand for services that can provide insights and enhance decision-making.
The emergence of IoT information managers has opened up new avenues for innovation and efficiency across various sectors. Here are some ways in which this new frontier is impacting industries:
- Healthcare: Information managers facilitate better patient monitoring and healthcare delivery by aggregating and analyzing health data from wearable devices and home monitoring systems.
- Manufacturing: In the manufacturing sector, these managers help optimize production processes by providing real-time data on equipment performance and maintenance needs.
- Smart Cities: Information managers play a crucial role in managing the vast amounts of data generated by smart city infrastructure, such as traffic management systems and energy grids, leading to more efficient urban planning and resource allocation.
As this sector continues to evolve, it is poised to become an integral part of the digital ecosystem, driving advancements in technology and enhancing the way we interact with and benefit from connected devices.
Emergence of IoT Data Brokers
The rise of interconnected devices has led to a new era in information management. As these devices proliferate, so does the need for specialized entities to handle the vast amounts of information they generate. This section delves into the advent of these entities, examining their impact on privacy and security in the digital landscape.
The proliferation of smart devices has necessitated the emergence of intermediaries who specialize in managing and distributing the information these devices produce. These intermediaries play a crucial role in the ecosystem, facilitating the flow of information between device manufacturers, service providers, and end-users. However, their activities also raise significant concerns regarding the protection of personal information and the overall security of the network.
One of the primary challenges posed by these intermediaries is the potential for unauthorized access to sensitive information. As they collect and disseminate vast amounts of data, the risk of breaches increases. This not only threatens individual privacy but also has broader implications for national security and economic stability. Therefore, it is imperative to establish robust safeguards and regulatory frameworks to mitigate these risks.
Moreover, the integration of these intermediaries into the fabric of daily life has led to an increased dependence on digital infrastructure. This reliance on technology, while beneficial in many ways, also exposes vulnerabilities that can be exploited by malicious actors. Ensuring the integrity and security of this infrastructure is thus a critical concern that requires ongoing attention and investment.
In conclusion, the emergence of these intermediaries in the realm of interconnected devices marks a significant shift in how information is managed and utilized. While they offer substantial benefits in terms of efficiency and connectivity, they also introduce new challenges that must be addressed to protect privacy and ensure security. As the landscape continues to evolve, it is crucial to develop comprehensive strategies that balance the benefits of these technologies with the need for robust protections.
Impact on Privacy and Security
As information handlers proliferate in the digital realm, the implications for individual privacy and overall security become increasingly complex. This section delves into how these entities, which aggregate and distribute vast amounts of personal information, affect the safeguarding of sensitive details and the integrity of security measures.
Privacy concerns are paramount as these information aggregators collect and analyze personal details without direct user consent. This practice can lead to unauthorized access to confidential information, potentially exposing individuals to risks such as identity theft and financial fraud. Moreover, the lack of transparency in how this information is used and shared exacerbates these privacy issues.
Security is another critical aspect affected by the operations of these information handlers. The integration of collected details into various systems and platforms can create vulnerabilities if not properly secured. Cyber threats, such as hacking and malware, target these centralized repositories of personal information, posing significant risks to both individual users and broader network security.
Furthermore, the global nature of digital information exchange complicates regulatory compliance. Different regions have varying laws and standards regarding privacy and security, making it challenging for these entities to operate uniformly while adhering to diverse legal frameworks. This discrepancy can lead to legal conflicts and undermine the effectiveness of security measures.
In conclusion, the proliferation of information handlers in the digital space necessitates a robust framework that balances the utility of collected information with the protection of individual privacy and the enhancement of overall security. Addressing these challenges requires not only technological solutions but also comprehensive legal and ethical standards to guide the responsible use of personal information.
Future Trends in IoT Data Management

As the landscape of interconnected devices continues to evolve, the management of information generated by these devices is poised for significant transformations. This section explores emerging patterns and innovations that are likely to shape the way we handle and utilize information from smart devices in the coming years.
One of the most prominent trends is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into device management systems. AI can enhance the efficiency and accuracy of information processing, enabling more sophisticated analysis and decision-making capabilities. Additionally, the adoption of blockchain technology is expected to increase, providing a more secure and transparent framework for recording and sharing information across networks.
Another significant trend is the shift towards edge computing, which involves processing information closer to where it is generated. This approach reduces latency and bandwidth usage, making it particularly beneficial for real-time applications and large-scale deployments. Furthermore, there is a growing emphasis on interoperability, ensuring that devices from different manufacturers can communicate and work together seamlessly.
| Trend | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| AI Integration | Incorporation of artificial intelligence to enhance data processing and analysis. | Improved efficiency and decision-making capabilities. |
| Blockchain Adoption | Use of blockchain technology for secure and transparent data recording and sharing. | Enhanced security and trust in data transactions. |
| Edge Computing | Processing data closer to the source to reduce latency and bandwidth usage. | Better real-time performance and scalability. |
| Interoperability | Ensuring devices from different manufacturers can communicate effectively. | Increased flexibility and compatibility in device networks. |
In conclusion, the future of information management in the realm of interconnected devices is rich with potential. By embracing these emerging trends, we can look forward to a more efficient, secure, and interconnected world where smart devices play a pivotal role in our daily lives.




